Test for CD123: A key marker due to its high expression (~95%) on BPDCN cells2-4
CD123, as part of a signature marker triad with CD4 and CD56, is a key marker in identifying BPDCN—a disease that can be challenging to distinguish from other hematologic malignancies.1,2
Signature marker triad1,2*


Key features of CD123 expression
- Highly expressed (~95%) on BPDCN cells and negligibly expressed on healthy cells2-5
- Can be both a diagnostic marker and a therapeutic target in BPDCN5
*BPDCN diagnosis can include other markers, such as TCL1, TCF4, and CD303 (BDCA2).1,6
BPDCN is a pathologic diagnosis based on immunophenotype analysis through immunohistochemistry or flow cytometry1
Diagnosis of BPDCN requires multiple positive and negative markers1†
| Antigens that confirm the diagnosis of BPDCN1,6 | Antigens that exclude the diagnosis of BPDCN2,3,7-11 | Other markers that may be positive in BPDCN7,8 |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
†One or more of these markers may be negative in some cases of BPDCN. Negativity does not rule out the diagnosis but does make it less likely.1,8
BPDCN, blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm; TdT, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase.
Recognizing BPDCN: Morphology
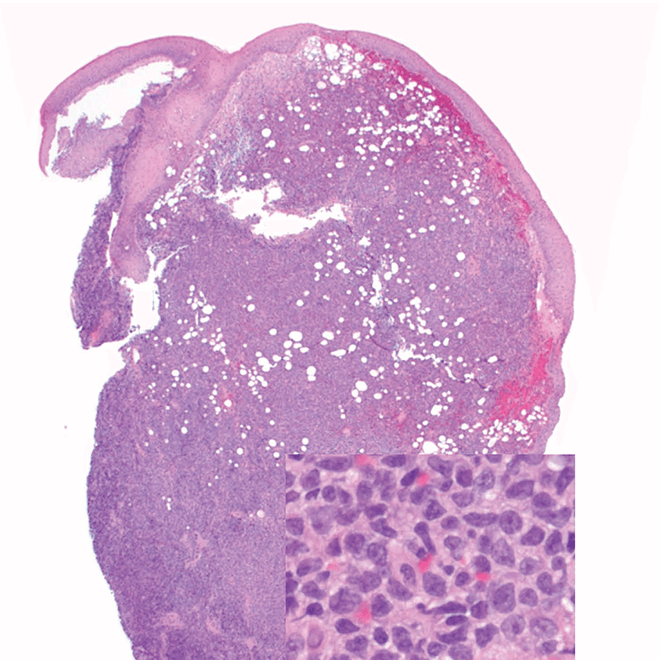
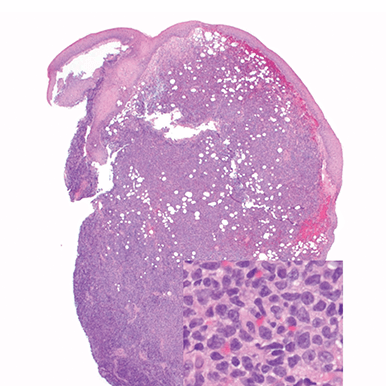
- Skin
- Punch biopsy of a skin lesion showing BPDCN (H&E stain, x40) and (inset) medium-sized malignant cells spare the epidermis (H&E stain, x1000).11
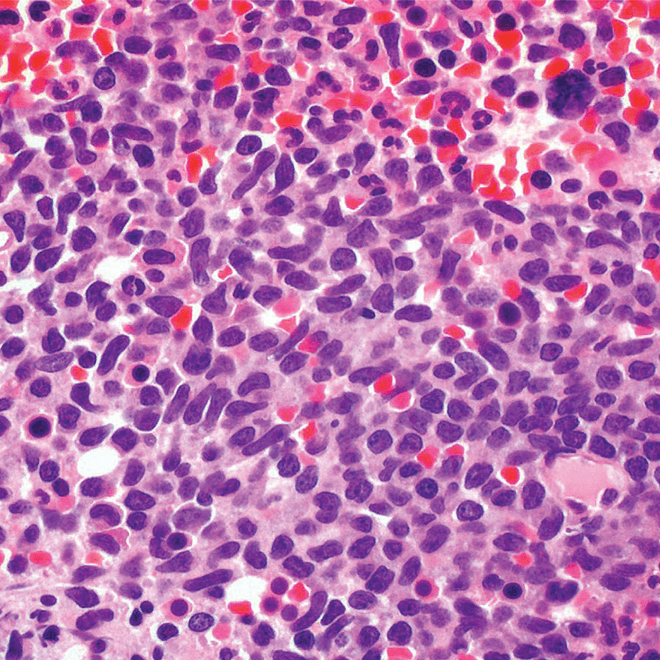
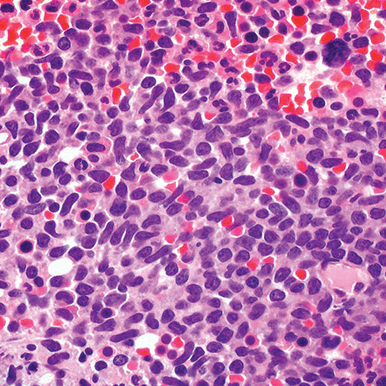
- Bone marrow
- Core biopsy showing diffuse infiltrate by BPDCN (H&E stain, x600).11
-
H&E, hematoxylin and eosin.
Reprinted by permission of SAGE Publications, Inc.
Main morphologic features of BPDCN biopsy
- Diffuse, monomorphic infiltrate1
- Medium-sized blast cells with irregular nuclei1
- Fine chromatin1
- At least 1 small nucleolus1
- Malignant BPDCN cells do not typically infiltrate the epidermis4
BPDCN with low-density infiltrate may mimic an inflammatory condition4
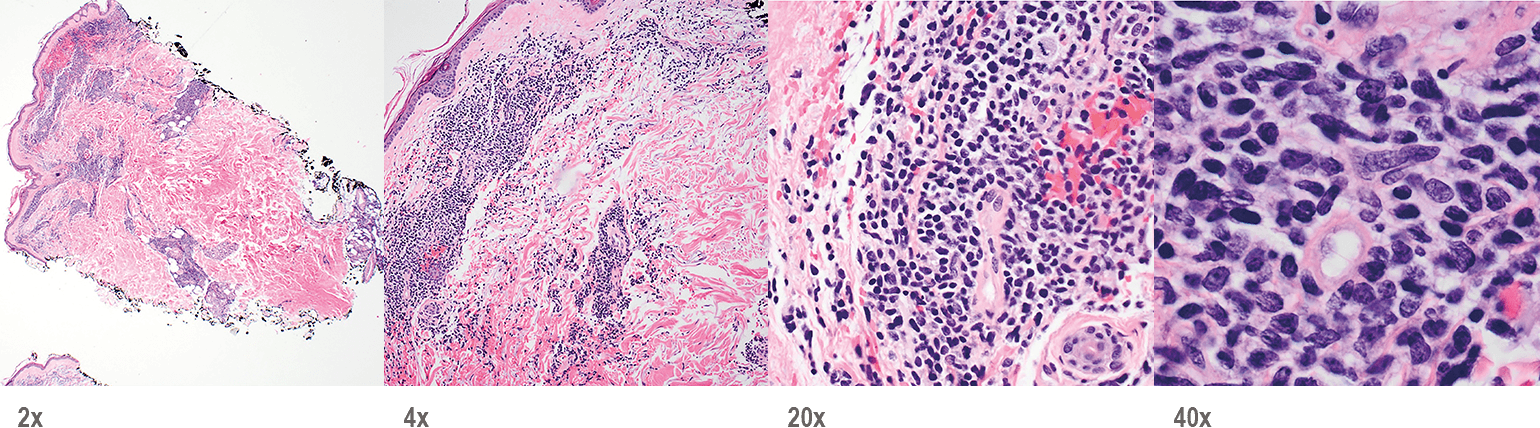
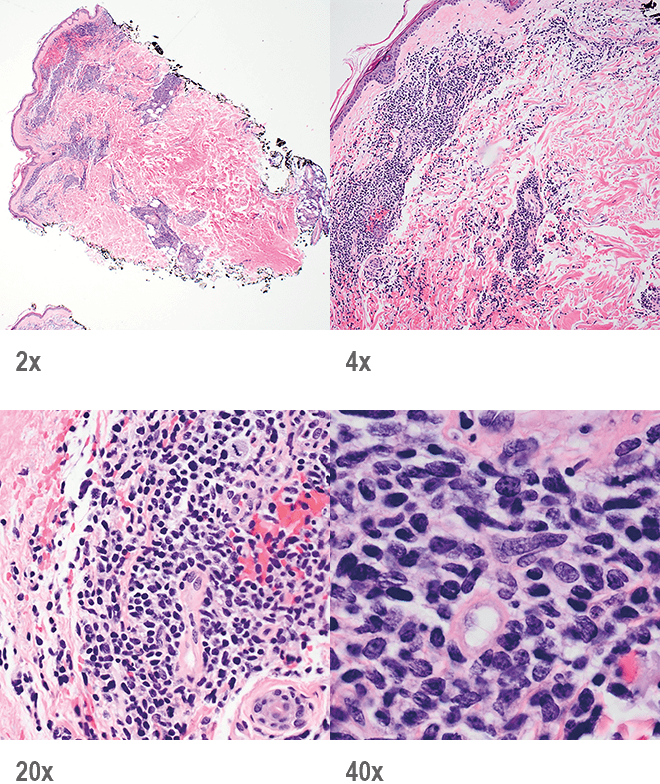
Image provided by Sheeja Pullarkat, MD.
- Cutaneous cases with minimal involvement show periadnexal and perivascular infiltrate, clustering in the superficial to mid dermis12,13
- Cytology, in association with flow cytometry immunophenotyping and clinical history, can help obtain an accurate diagnosis of BPDCN14
To help with a timely and accurate diagnosis, consider including CD123, CD4, and CD56 in early diagnostic panels1,2
- References:
- Pagano L, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: diagnostic criteria and therapeutical approaches. Br J Haematol. 2016;174(2):188-202.
- Pagano L, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm with leukemic presentation: an Italian multicenter study. Haematologica. 2013;98(2):239-246.
- Laribi K, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: from origin of the cell to targeted therapies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22(8):1357-1367.
- Facchetti F, et al. Neoplasms derived from plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Mod Pathol. 2016;29(2):98-111.
- Frankel AE, et al. Activity of SL-401, a targeted therapy directed to interleukin-3 receptor, in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm patients. Blood. 2014;124(3):385-392.
- Ceribelli M, et al. A druggable TCF4- and BRD4-dependent transcriptional network sustains malignancy in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. Cancer Cell. 2016;30(5):764-778.
- Cronin DMP, et al. Immunophenotypic analysis of myeloperoxidase-negative leukemia cutis and blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. Am J Clin Pathol. 2012;137(3):367-376.
- Sangle NA, et al. Optimized immunohistochemical panel to differentiate myeloid sarcoma from blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. Mod Pathol. 2014;27(8):1137-1143.
- Deotare U, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm with leukemic presentation: 10-Color flow cytometry diagnosis and HyperCVAD therapy. Am J Hematol. 2016;91(3):283-286.
- Garnache-Ottou F, et al. Extended diagnostic criteria for plasmacytoid dendritic cell leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2009;145(5):624-636.
- Riaz W, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: update on molecular biology, diagnosis, and therapy. Cancer Control. 2014;21(4):279-289.
- Reichard KK. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: how do you distinguish it from acute myeloid leukemia? Surg Pathol Clin. 2013;6(4):743-765.
- Sullivan JM, Rizzieri DA. Treatment of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2016;2016(1):16-23.
- Ferreira J, et al. Cytomorphological features of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm on FNA and cerebrospinal fluid cytology: a review of 6 cases. Cancer Cytopathol. 2016;124(3):196-202.




